The Journey Beyond Industry 4.0 – Embracing Smart Manufacturing

If you missed the initial article in our series, be sure to check it out Cybersecurity in the Manufacturing Industry. This was launched alongside the Industrial Cyber Industrial Cybersecurity Handbook for Manufacturing. This article series focuses on the pressing cybersecurity challenges within the industry, aiming to encourage proactive steps in this crucial field. And now, let’s dive into Part 2.

Industry 4.0 is far more than a fleeting trend in the manufacturing sector; it represents a seismic shift in how things are constructed, merging digital technology with traditional industrial methods. Known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, this era is defined by the integration of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It heralds a transformative phase, where modern digital technology is interwoven into manufacturing, giving rise to what is often termed a ‘smart factory’.
At the core of Industry 4.0, we find the Internet of Things (IoT) and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Imagine everything, from your car to your coffee maker, hooked up with smart tech, chatting away and making decisions. In the industrial world, IIoT cranks this up a notch, leading to machines that not only talk to each other but also make smart decisions on their own. Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) are also a big deal here, blending computing, networking, and physical processes into one smooth operation.
Then there’s Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics, the heavy lifters of Industry 4.0. They’re like brains, storing huge amounts of data and making sense of it all. And let’s not forget Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning – these are the whizzes that automate complex tasks and spot things we humans might miss. Additive Manufacturing, like 3D printing, is pushing boundaries too, offering custom solutions and cutting down waste. And for a bit of sci-fi in real life, we’ve got Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) stepping in for training, remote maintenance, and making product design super cool.
Robots and automation? Absolutely central to Industry 4.0. They’re the muscle, doing the heavy lifting, repetitive tasks, or the stuff that’s too risky for humans, all while boosting efficiency and slashing errors. And as everything gets more connected and data-dependent, Cybersecurity is becoming a big watchword – it’s all about keeping the data safe and sound.
The real magic of Industry 4.0 is how it ties all these elements together, making manufacturing more efficient, responsive, and automated. It’s a whole new way of designing, making, and distributing products, leading to smarter work, better productivity, and opening doors to innovative business models.
Remember those history classes about industrial revolutions? From steam engines to electricity, and then computers automating factories? Well, now we’re marching into the age of TOTAL AUTOMATION – think smart manufacturing on steroids.
The real challenge lies in shifting from basic automation to smart manufacturing, a realm where automated systems join forces with big data and AI. This transition isn’t just about ramping up efficiency; it introduces a complex array of cybersecurity challenges. These challenges echo those familiar in the IT world but come with their unique twists and intricacies. It’s a balancing act between harnessing the power of advanced technology and navigating the heightened cybersecurity landscape that accompanies it.

The Tale of Two Technologies
OT and IT can be likened to siblings with distinct traits. IT is all about data and the corporate world, typically overseen by tech chiefs. OT is more about the hands-on manufacturing processes, managed by the factory floor gurus. Here’s what sets them apart: Patching in IT jumps on updates quickly, whereas OT often sees them as a hassle. Architecture in IT focuses on data transactions, while OT is all about the production process. Communication Protocols in IT use general protocols, while OT has its own unique set.
While IT prioritizes data security, OT is more about keeping the production line humming along. Now, as smart technologies emerge, OT is encountering IT-style cybersecurity risks, including Network Isolation Blunders, Configuration Slip-ups, Invisible Assets, Update Quandaries, and Supply Chain Sneak Attacks.
The Purdue Model: A Blueprint for Cybersecurity in Manufacturing
Enter the Purdue Model or Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture. This is like the master plan for keeping industrial control systems safe and sound, focusing on layered defenses and smart network setups. Manufacturers must build solid defense layers and sort their assets smartly.
The Purdue model is an architectural blueprint for OT/ICS security, focusing on the segmentation of various components such as physical processes, sensors, supervisory controls, operations, and logistics. It has become a crucial framework for ICS network segmentation, safeguarding OT from threats like malware, particularly with the advent of edge computing and direct-to-cloud connectivity.
This model delineates the typical elements in an ICS architecture, dividing them into distinct zones encompassing both IT and OT systems. When applied effectively, it facilitates the creation of a buffer zone (gap) between ICS/OT and IT systems, allowing for robust access control without impeding operational efficiency.
The Purdue Model divides an industrial network into several layers, ranging from physical equipment at the lowest level to corporate systems at the highest. These layers include:
- Level 0: Physical process (sensors, actuators).
- Level 1: Intelligent devices (control systems like PLCs).
- Level 2: Supervisory control (SCADA systems).
- Level 3: Operations management (MES systems).
- Level 3.5: The IT/OT Demilitarized Zone (iDMZ)
- Level 4: Business logistics systems.
- Level 5: Enterprise network
- Level 6: Cloud and Beyond?
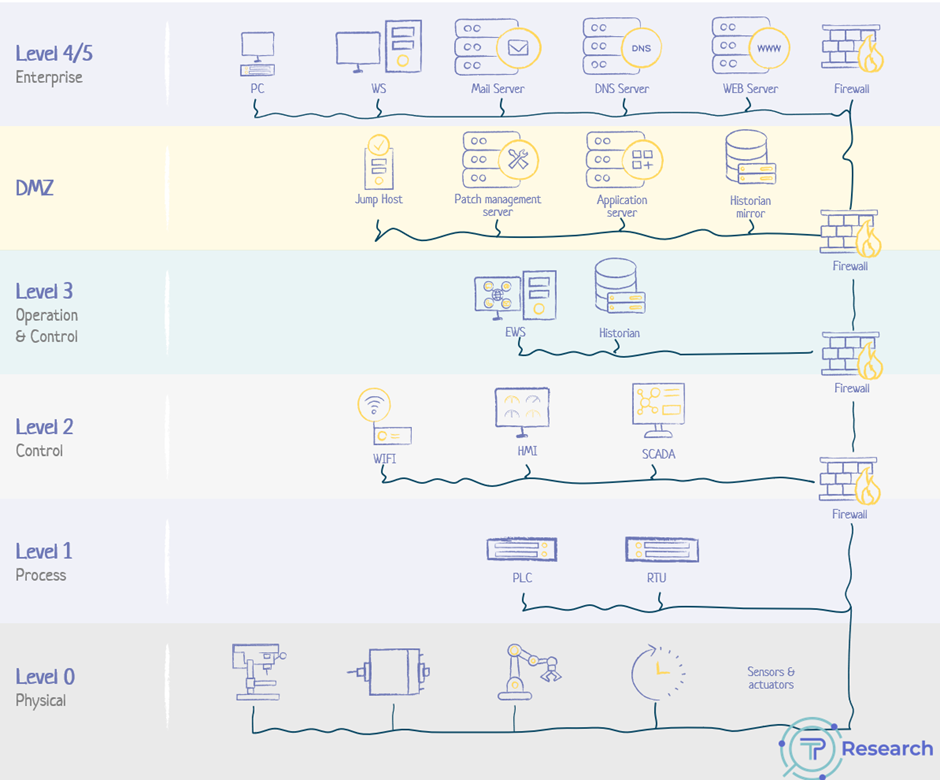
The Infamous Purdue Model
Although the Purdue Model has aged, it remains a vital tool for many manufacturers. It stands as a guiding light, aiding in the construction of robust defense systems. This model excels in its approach to categorizing assets with similar security needs and managing them effectively. Despite the passage of time, its relevance in organizing and securing manufacturing systems is still widely recognized and valued.
Remember, Securing the Cloud is Crucial!

In today’s manufacturing landscape, there’s a heavy reliance on IIoT and cloud computing for enhanced efficiency and insightful data analysis. This shift to cloud-based solutions brings its own set of challenges, including cloud security complexities, network vulnerabilities, and risks surrounding data and software security. It’s important to recognize that cloud security isn’t just someone else’s problem; it’s a critical component of a manufacturer’s overall cybersecurity strategy.
To mitigate these risks, manufacturers must strike a balance between accessibility and security. Implementing an asset lifecycle security framework can offer comprehensive IT/OT cybersecurity, especially when integrating cloud tech.
The aim is to pinpoint that perfect balance that empowers business operations and ensures safety, all while safeguarding critical systems. By adopting a risk-based approach, manufacturers can more effectively navigate toward this goal. This method involves carefully evaluating potential risks and making informed decisions to mitigate them, ensuring both operational efficiency and robust security are maintained.
In a nutshell, as Industry 4.0 keeps evolving, it’s not just about getting slicker and more innovative; it’s also about facing up to some serious cybersecurity and system integration challenges. It calls for a strategic focus on trustworthy assets and solid security plans to keep everything running smoothly and safely.
And remember, safety should always be at the forefront – both physical and cyber safety are paramount in any operational environment. Prioritizing these aspects ensures a secure and efficient manufacturing process.










