Dragos reports decline in ransomware attacks on industrial sector amid law enforcement measures
Industrial cybersecurity firm Dragos has identified that hackers have targeted industrial control systems (ICS) equipment, with the engineering sector experiencing 12.4 percent of the reported attacks across 21 incidents. Dragos observed unique developments in the ransomware landscape during the first quarter of this year, including notable successes in law enforcement actions and unexpected shifts in the behavior of cybercriminals, although ransomware continues to pose a significant threat to industrial organizations globally.
“Dragos has noted a decline in ransomware activities targeting the industrial sector in the first quarter of 2024 compared to the final quarter of the previous year,” Abdulrahman H. Alamri, senior adversary hunter at Dragos, wrote in a Thursday blog post. “Of the 77 ransomware groups known for their industrial attacks, just 22 remained active recently, a decrease from 32 in the earlier quarter. Similarly, the number of ransomware incidents within the industrial sector reduced from 204 to 169.”
Alamri identified that the downturn is attributed, with moderate confidence, to a shift in focus by ransomware groups towards the healthcare sector since early 2024 and a significant increase in law enforcement actions dismantling ransomware operations and apprehending the individuals involved.
Furthermore, Alamri noted that unlike in previous periods, there were no significant operational disruptions caused by ransomware in the first quarter of 2024. “While this might initially seem optimistic, the emerging trend of ransomware groups influencing their affiliates to shift focus and maximize impact on specific sectors raises concerns. Dragos assesses with moderate confidence that such coordinated efforts pose a real threat to the industrial sector, especially if similar tactics are adopted in the future.”
He assesses with moderate confidence that the ransomware threat landscape will continue to evolve, likely characterized by the introduction of new variants and an increasing number of coordinated campaigns targeting industrial sectors. Ransomware groups are anticipated to further refine their strategies, with a high probability of continuing to leverage zero-day vulnerabilities in their attacks.
“Additionally, there are only two ransomware variants that have demonstrated OT-impacting capabilities – EKANS and Cl0p. However, Dragos is aware of multiple instances where ransomware operators were able to detonate ransomware within the OT environment and, even without OT-impacting capabilities, was still able to cause operational disruption,” Alamri disclosed. “For those reasons, ransomware operators considering how their respective criminal enterprises can better impact industrial organizations and OT environments is entirely plausible. This is further exacerbated by industrial trends of digitalizing OT environments and movement towards more IT and OT connectivity and dependencies.”
Alamri said that this potential shift in focus towards OT processes and environments could be driven by the continuous attempts of ransomware groups to exert greater pressure on victims to pay ransom. “By targeting critical OT processes, these groups could significantly amplify the impact of their attacks on industrial organizations. Such disruptions would not only affect operational capabilities but also compromise safety, thereby increasing the urgency and potentially compelling victims to meet ransom demands more readily.”
He pointed out that this evolving strategy reflects a concerning trend in the ransomware landscape, where the consequences of attacks extend beyond data loss and financial impact to directly threaten the core operational integrity of targeted organizations.
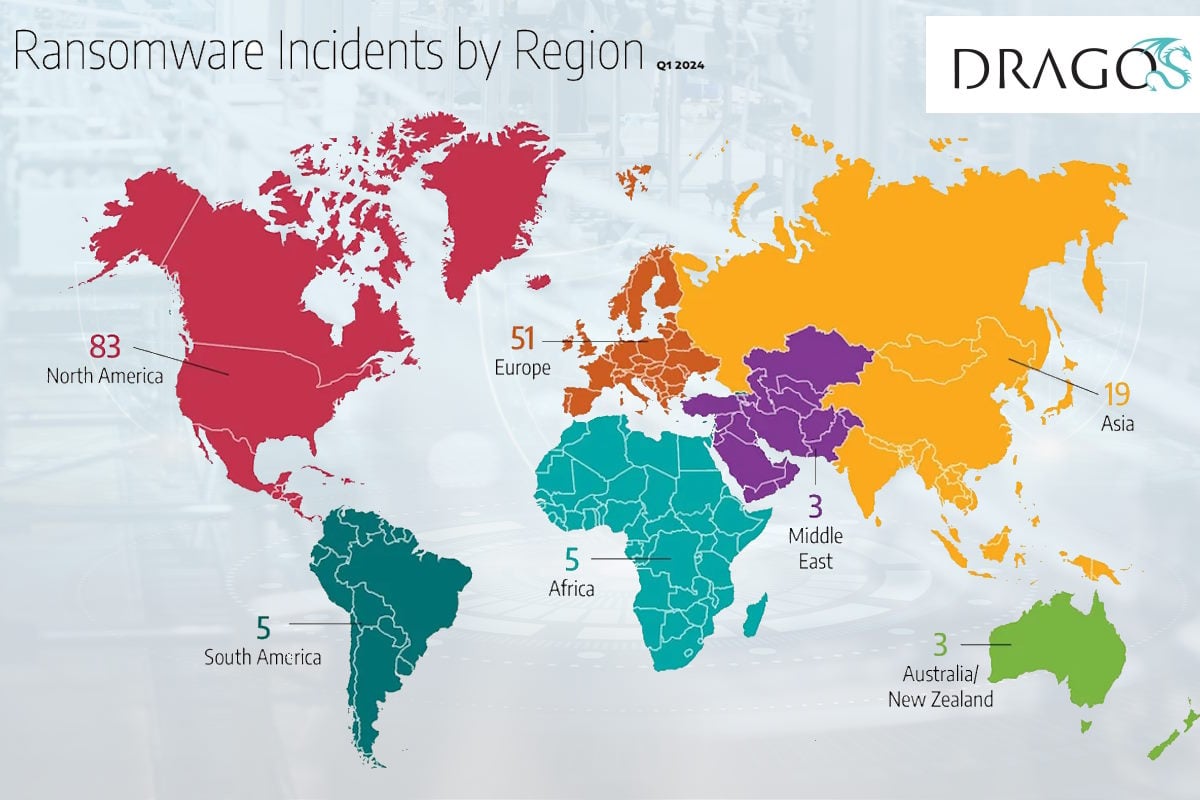
Dragos identified 83 ransomware incidents (roughly 49 percent of the observed 169 global ransomware attacks) that impacted industrial organizations and infrastructure in North America, compared to 87 incidents in the previous quarter. Within North America, the U.S. received over 45 percent of all ransomware incidents, compared to 37 percent in the previous quarter.
Approximately 30 percent of global ransomware incidents (51 in total) impacted Europe, compared to 67 incidents in the previous quarter. Asia is next with approximately 11 percent, or 19 incidents, with South America and Africa having roughly 3 percent, or five incidents each; and the Middle East and Australia faced three incidents, each.
Alamri disclosed that manufacturing was the most impacted industry during the first quarter of 2024, with 106 observed incidents in total, or 62.7 percent. The transportation sector was impacted 25 times, for a total of 14.7 percent of all observed incidents, while the ICS equipment and engineering sector had 12.4 percent of alleged attacks. Also, the oil and natural gas sector had 4.3 percent of alleged attacks (8 incidents), which is double the number of incidents of the previous quarter; the water and wastewater sector was the victim of 1.7 percent of alleged attacks (three incidents); and mining, communications, electric, and renewable energy sectors had two or less attacks each in the last quarter.
Dragos’ analysis of numerous ransomware data from the first quarter of 2024 indicates that the Lockbit 3.0 group was behind the most attacks against industrial organizations, with 26.6 percent or 45 incidents of observed ransomware events. The 8base ransomware was the second with 13.6 percent or 23 incidents.
Some of the observed ransomware group trends for the first quarter of the year included Hunters International was responsible for 17 incidents, representing 10.06 percent; Black Basta was linked to 13 incidents, which is 7.69 percent; Akira accounted for 12 incidents, translating to 7.10 percent; and Alphv was involved in 11 incidents, equating to 6.51 percent.
Furthermore, Cactus was identified in nine incidents or 5.33 percent; Bianlian was responsible for eight incidents, or 4.73 percent; MedusaLocker was active in five incidents, making up 2.96 percent; both Play and Trigona were associated with four incidents each, each holding 2.37 percent; Inc Ransom and Stormous, each had a hand in three incidents, each with 1.78 percent; Meowleaks, Qilin, and Rhysida were each tied to 2 incidents or 1.18 percent; and Abyss, Blacksuit, Cl0p, Cuba, Knight, and Ransomexx were each involved in one incident.
The groups that Dragos observed in the fourth quarter of last year, but not in the first quarter of this year, include Losttrust, Noescape, RA Group, Lorenz, MetaEncryptor, MoneyMessage, Snatch, Threeam, DoNut Leaks, Daixin Team, Monti, and RagnarLocker.
Alamri mentioned that an extensive international law enforcement collaboration led to the dismantling of the Lockbit ransomware group, one of the most prominent and widely recognized groups in the cybercrime arena. “Concurrently, the Alphv/Blackcat group, another prominent player in the ransomware ecosystem, initiated a surprising self-decommission of its infrastructure after stealing millions of dollars from an affiliate that recently attacked an American healthcare services provider.”
The recent Alphv/BlackCat ransomware campaign targeting the healthcare sector is particularly concerning. The effects go beyond financial losses, directly threatening human lives and healthcare services. The situation highlights the powerful influence that leading ransomware groups wield over their affiliates, guiding them to concentrate attacks on specific industries to amplify damage. Furthermore, this reflects a strategic refinement in ransomware tactics, transitioning from merely targeting individual victims to orchestrating operations aimed at deliberately targeting specific industry.
Dragos assesses with moderate confidence that this type of coordinated effort could become a substantial threat to industrial sectors if similar tactics are applied in the future. This risk is amplified as ransomware payment rates decline and law enforcement agencies increase successful takedown campaigns against ransomware groups.
“The technical capabilities of ransomware groups in the first quarter of 2024 underscore their agility and sophistication in exploiting vulnerabilities, particularly in public-facing applications,” the post added. “The targeting of ConnectWise ScreenConnect by BlackBasta and Lockbit and the Qlik Sense application by CACTUS highlight a strategic approach to leverage weak points in widely used platforms. Furthermore, the rapid exploitation of new vulnerabilities, as demonstrated by Cactus exploiting a vulnerable VPN less than 24 hours after the vulnerability was initially disclosed, showcases these groups’ swift adaptability and readiness to capitalize on security gaps.”
Moreover, Dragos has assessed with moderate confidence that ransomware operations, possibly in collaboration with initial access brokers (IABs), have attempted to exploit zero-day vulnerabilities in Ivanti ICS VPN.
In February, Dragos disclosed that it has been tracking activity by the Voltzite threat group, which overlaps with Volt Typhoon, since early 2023. The group has been observed performing reconnaissance and enumeration of multiple U.S.-based electric companies since early 2023, and since then has targeted emergency management services, telecommunications, satellite services, and the defense industrial base.










